
What is key management?
Comprehensive key management for maximum security
Sensitive data is a valuable asset that companies protect through encryption (data encryption). If this is not done, data and security breaches may occur, leading to financial losses and reputational damage. Often, different tools are used for encryption, making key management even more complex. To maintain oversight, key management solutions are helpful. Especially in the area of cloud key management, flexible and secure solutions are becoming increasingly important.
A KMS centrally manages the keys required for cryptographic procedures within a company, provides timely reminders before they expire, and supports the entire key lifecycle.

In a company’s infrastructure, a wide variety of keys and certificates are in use. Employees access the infrastructure not only from their workplaces. Increasingly, network devices (e.g., printers), tablets, and mobile devices are being integrated, and access from home offices is also enabled. All data transmitted or received by these devices should be sent as encrypted data.
Cryptographic keys and digital certificates
Cryptographic keys serve to sign and encrypt information. To associate the keys with an identity, digital certificates are required. A company can generate these itself via its internal Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). However, certificates issued by an external certification authority (Certificate Authority, CA) are generally considered more trustworthy.
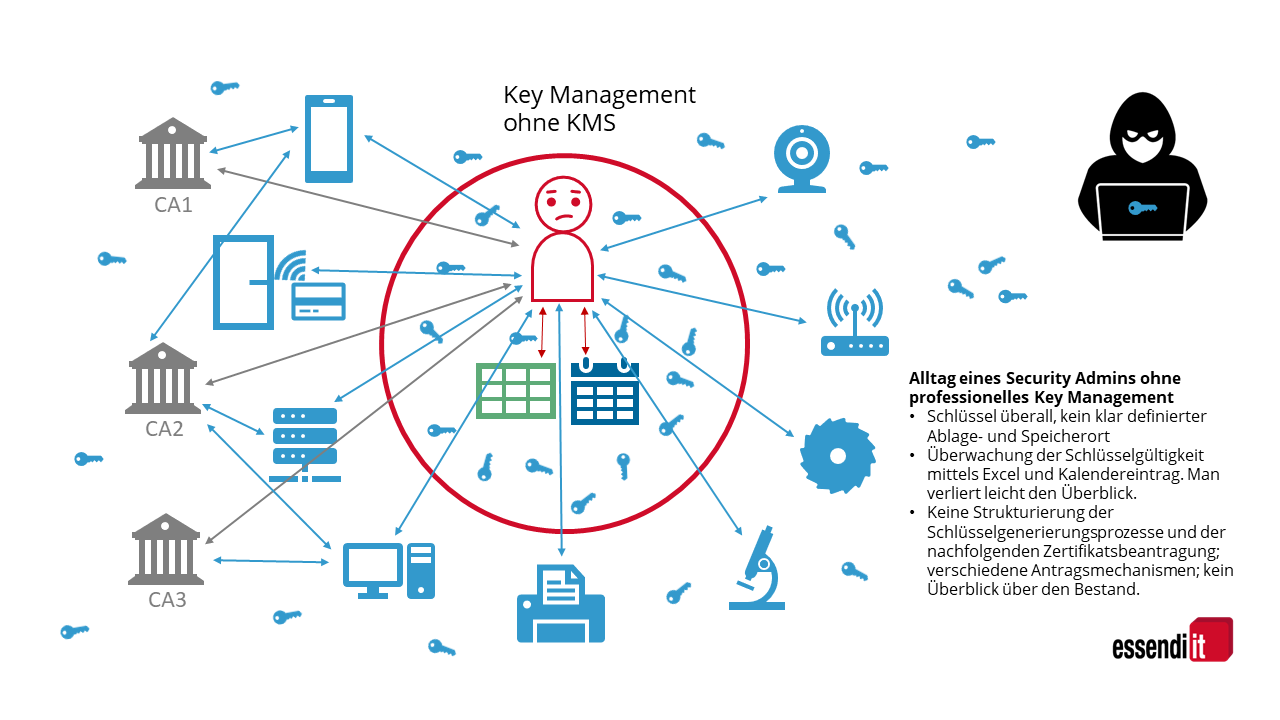
Key Management in the Internet of Things (IoT)
In every corporate network, cryptographic keys are used, usually in connection with digital certificates. For example, emails or other documents can be provided with digital signatures. In addition, more and more keys are now being used for IoT devices such as production machines, access control systems, or surveillance cameras, since industry standards recommend encryption during data exchange to protect these devices. This poses an additional challenge in terms of data security and data protection.
Key Management System (KMS)
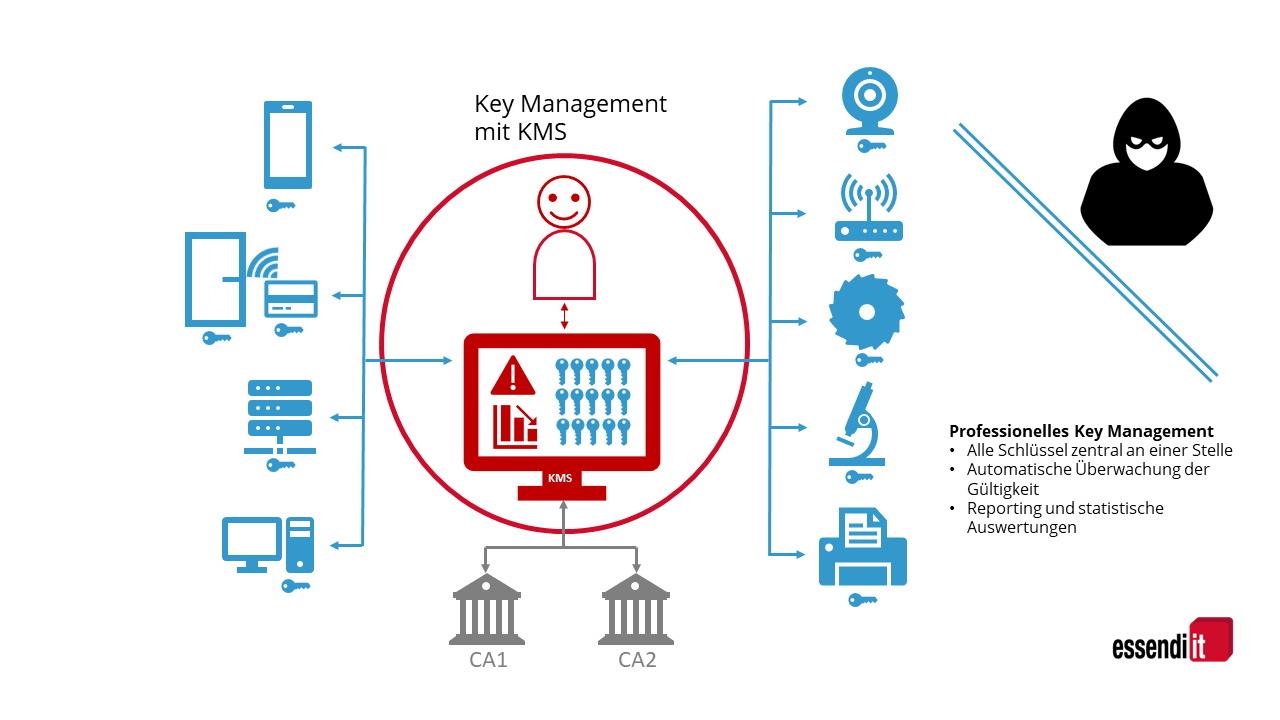
It is therefore advisable to rely on a key management service (KMS). A KMS centrally manages the keys required for cryptographic procedures within a company, provides timely reminders before they expire, and supports the entire key lifecycle. An important step in this process is KMS activation, which enables access to key management.
A centralized enterprise key management system therefore makes it easier to keep track of the cryptographic keys used in the company and thus prevents unauthorized access. At the same time, the validity of the certificates and keys in use is effectively monitored and controlled. In this way, all cryptographic keys are managed uniformly and automatically.
Key management ensures that the key is genuine and kept secret. It can generate, store, provide, exchange, and protect a large number of keys. Professional tools also offer the ability to integrate Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) to generate or store keys. Within them, keys are managed even more securely, and a higher level of security can be achieved. Depending on the HSM manufacturer, audit-compliant reports can additionally be retrieved, contributing to audit security. A structured key management system also helps to efficiently meet strict compliance requirements. In addition, automated key management is more reliable than error-prone manual methods such as Excel lists.
Im asymmetrischen Verschlüsselungsverfahren mit öffentlichen (public keys) und privaten Schlüsseln (private keys) stellt das KMS sicher, dass ein öffentlicher Schlüssel auch wirklich der übermittelnden Person oder Maschinenidentität gehört und zum privaten Schlüssel passen. Zur Prüfung kontaktiert sie eine Certificate Authority (CA) oder ein Trust Center (TC). Ergänzend werden Schlüssel und Zertifikate über gesicherte Pfade an die Zielsysteme übertragen.
Objectives of key management
Key management includes the following objectives:
- Secure management of large key volumes, centralized overview
- Management of keys and control of all encryption keys used in the company
- Including support for various standards and key types
- Protection of keys against hackers and unauthorized access
- Access to the keys only for authorized persons
- Audit security through compliance with regulations and legal requirements
- Analyzability of the encryption keys available in the company. Detection of vulnerabilities and proactive replacement
- process automation
Functions of key management
Key management includes, among other things, the following functions:
- Secure communication, e.g., with CAs and TCs
- Generating cryptographic keys using various encryption and signature algorithms
- Storage and provision of key material
- Secure transmission of keys
- Revoking and destroying compromised or invalid keys
- Logging of actions related to the keys in the KMS
- A KMS server manages the keys centrally and ensures their secure distribution and storage.
The Key Management Interoperability Protocol (KMIP)
Applications and systems must therefore be able to exchange information securely with key management systems. For this purpose, the Key Management Interoperability Protocol (KMIP) was developed. KMIP makes this possible. Through this standardized communication protocol, different systems can be linked for cryptographic operations. In this way, centralized key management is enabled.
A special case is the encryption of cloud data. Data stored in the cloud must be protected from unauthorized access by the cloud provider (e.g., Amazon Web Services). Keys make it possible to securely encrypt and decrypt data and thus protect confidential information. The associated keys must therefore be stored separately from the sensitive data. In such cases, hardware-based modules are used. The Key Management Service of Amazon Web Services (AWS KMS) offers a BYOK option (Bring Your Own Key). For Microsoft 365, on the other hand, there is Double Key Encryption (DKE).
Hardware security modules
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) often provide optimal or enhanced protection and allow a higher level of security to be achieved. HSMs are independent hardware components used to secure cryptographic processes. They are suitable for generating signature and encryption keys and offer services to perform cryptographic operations with the keys. One example of this is certifying blockchain transactions.
Since the decryption of cloud data is only possible via the separate and tamper-proof HSM, an additional layer of security is created. In addition, depending on the manufacturer, some HSMs also have a functionality that causes them to self-destruct if tampering is detected, e.g., opening or unscrewing the hardware.
An example of a key management service is the one provided by AWS (Amazon Web Services). AWS KMS uses validated hardware security modules and a so-called KMS key (Key Management Service Key). This fail-safe service makes it possible to centrally create, manage, and protect cryptographic keys.
Key management in the context of standards (DIN EN ISO/IEC 27001, National Institute of Standards and Technology / NIST Framework)
The fact that the proper management of cryptographic keys (encryption keys) is a relevant topic is demonstrated by their mention in ISO 27001 and in the NIST Framework. In the course of establishing an Information Security Management System (ISMS), ISO 27001 requires in Annex point A.10 the use of cryptography within the company. The standard requires
- Defining policies for the use of cryptographic measures to protect information
- Developing a policy for the use, protection, and lifetime of cryptographic keys and implementing their entire lifecycle (key management)
In addition, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the USA has defined a framework that provides guidance for the design and implementation of cryptographic key management (A Framework for Designing Cryptographic Key Management Systems). This also addresses the definition of policies, standards, and roles for the secure handling of keys. It also clarifies the requirements that must be met by a KMS tool.
essendi xc. Simple and smart.
In essendi xc, integration options for HSMs from well-known providers are provided to ensure the high level of protection required for your key material and/or to connect HSMs already in use in the SSL/TLS environment.
As a comprehensive management system for all types of X.509 certificates (CKMS), essendi xc covers the entire certificate lifecycle through key policies and status monitoring. It supports your organization in handling certificates and their keys: from application to installation to renewal or archiving of expired certificates. Since xc can generate audit-compliant and revision-proof reports, it supports the implementation of an ISMS in accordance with ISO 27001 and the NIST framework.
Our central dashboard provides you with a graphical overview of your certificate inventory using various charts. For example, you can analyze it by signature algorithm or by certification authority. Further information can be found at essendi xc.




